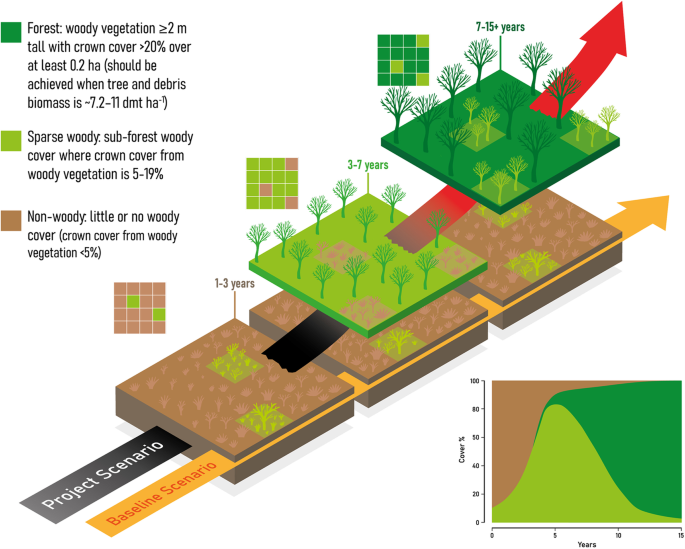
Key Takeaways:
Magnifying the Hidden Truth: Unveiling the Limited Impact of Australian Forest Regeneration Projects on Carbon Removals and Vegetation Changes
Australian Forest Regeneration Projects, aimed at restoring and conserving forested areas, have gained significant attention in recent years. While these projects are undoubtedly noble and contribute to environmental conservation efforts, their true impact on carbon removals and vegetation changes may not be as significant as initially perceived. In this article, we delve deeper into the underlying factors that constrain the effectiveness of these projects and explore potential solutions to magnify their impact.
The Hidden Challenges
Forest regeneration initiatives face several challenges that hinder their ability to achieve substantial carbon removal and vegetation changes. First and foremost, the scale and scope of these projects often fall short of what is truly necessary to counteract large-scale deforestation and degradation. While some efforts have successfully restored small patches of land, they are often overshadowed by the magnitude of the issue at hand.
Moreover, the effectiveness of forest regeneration projects heavily relies on factors such as land management practices, soil fertility, and biodiversity. In cases where land management techniques are inadequate or unsustainable, the regenerated forests may struggle to thrive and fulfill their intended purpose. Additionally, poor soil fertility and limited biodiversity can impede the growth and resilience of newly established vegetation, further limiting the overall impact of the projects.
Addressing Land Management
To maximize the effectiveness of Australian Forest Regeneration Projects, it is imperative to prioritize sound land management practices. This includes adopting sustainable reforestation techniques that minimize soil disruption and protect existing vegetation. By ensuring the long-term health and vitality of the regenerated forests, we can enhance their capacity for carbon sequestration and promote desirable vegetation changes.
Integrating advanced forest monitoring technologies can also aid in the identification of areas requiring additional attention and intervention. Through remote sensing techniques, scientists and project managers can closely monitor the progress of regeneration projects and assess the effectiveness of implemented strategies. This data-driven approach enables informed decision-making and offers valuable insights for future projects.
Promoting Ecosystem Preservation
While it is essential to restore deforested areas, it is equally important to preserve and protect existing forest ecosystems. Australian Forest Regeneration Projects should not only focus on planting new saplings but also emphasize the conservation of native flora and fauna. By safeguarding existing ecosystems, we can maintain biodiversity, encourage natural regeneration processes, and enhance the overall ecological balance.
This integrated approach to forest conservation ensures the continuity of carbon absorption and vegetation changes beyond the duration of individual regeneration initiatives.
Striving for Long-Term Sustainability
For Australian Forest Regeneration Projects to have a lasting impact on carbon removals and vegetation changes, it is crucial to adopt a comprehensive and holistic approach. This entails considering various interconnected factors and collaborating with multiple stakeholders, including local communities, scientists, policymakers, and landowners.
Implementing coordinated efforts that emphasize knowledge sharing, innovative techniques, and sustainable practices can address the inherent complexities and limitations of forest regeneration projects.
Engaging Stakeholders
Though forest regeneration is an ecological endeavor, it cannot succeed without active involvement from all stakeholders. Engaging local communities living around the restored areas fosters a sense of ownership, empowering them to become stewards of the environment. Through education and participatory programs, individuals can contribute to ongoing monitoring, maintenance, and regeneration activities, complementing the institutional efforts.
Policymakers play a pivotal role in creating an enabling environment for forest regeneration initiatives. By incentivizing sustainable land use practices, enacting stricter regulations against deforestation, and promoting research and development, they can pave the way for more effective and impactful projects.
Prioritizing Research and Innovation
Continued investment in research and innovation is key to unlocking new possibilities and overcoming existing limitations of forest regeneration projects. Collaborative research endeavors can help identify and develop plant species that are more resilient to changing climate conditions, making them better suited for reforestation efforts. Additionally, experimenting with novel techniques like assisted natural regeneration may offer cost-effective alternatives to traditional planting methods.
Key Takeaways:
- Australian Forest Regeneration Projects have a limited impact on carbon removals and vegetation changes.
- Australian Forest Regeneration Projects have a limited impact on carbon removals and vegetation changes.
FAQ
Do Australian Forest Regeneration Projects have any positive impact?
What factors affect the effectiveness of these projects?
How can the impact of these projects be magnified?
What is the long-term sustainability of Australian Forest Regeneration Projects?
Conclusion
[/myfaq]
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is based on current knowledge and understanding. Efforts have been made to ensure its accuracy; however, no guarantee can be given regarding the comprehensiveness, reliability, or suitability of this information for individual circumstances. This article should not be used as a substitute for professional advice or assistance. It is essential to consult with qualified professionals prior to making any decisions or taking any actions based on the information provided in this article.
Source: insidertechno.com